 |
page of student
|
|
|
|
SRWS
A process of interfusion of liquid in the reserved volume is the difficult physical phenomenon. In an order to analyse this phenomenon in relation to a concrete technological task the use of certain criteria which allow to execute comparative estimations. Within the framework of estimation of efficiency of interfusion of certain volume of liquid most often utillized the integrated index «intensity of interfusion». Intensity of interfusion of metal in a scoop appears a very important
technological index at treatment became on setting scoop-stove. At first, intensity of interfusion of metal is determined by duration of some stages of treatment, including homogenizations of metal on chemical composition and temperature or process of affinage of metal a slag. Secondly, the process of interfusion of metal gas takes a place difficultly enough, and both the areas of intensive circulation and «stagnant areas» the display of which can negatively affect eventual indexes of treatment on the whole appear in liquid bath. Thirdly, use of argon as a substance which provides the process of interfusion assumes additional charges on treatment and accordingly diminishing of amount of argon them, that is utillized, reduces. Basic tasks of physical design in relation to the real work it is possible to form thus: it is a study of features of interfusion of liquid in a scoop at its blowing out by gas through porous blocks, set in a bottom; it is a study of possibility of optimization of basic operating parameters of insufflation of gas (intensity, amount of продувных blocks, locations of продувных blocks, etc.) for providing of process of interfusion of rational intensity; it is a study of features of interfusion of metal with a slag in the process of blowing out of metal by gas.
Physical design
A physical design of processes of interfusion of liquid is most mainly at saving of identical geometrical sizes of the probed aggregate and model. However, volume of bulk of scoops which are utillized in a metallurgical production, 10-45 м3 (at mass of metal of 80-350 ?) makes, that does very difficult the technique of design with saving of geometrical sizes, as it is related to large labour intensiveness of research works and not always guarantees the receipt of absolutely reliable information on a physical design. Taking into account circumstance that at insufflation of gas in a liquid essential are processes, that weights which determine emerging of gas blisters are under the action of forces, and forces inertias which determine development of the system of circulation streams in liquid bath of scoop, in the real work as base criteria of similarity the criterion of Fruda and criterion of гомохронности was accepted. The physical design of process of interfusion of fusion rare gas in a scoop is executed on a transparent model, that allows визуализировать all of basic processes which take a place at blowing out of liquid. The geometrical sizes of capacity which imitates a сталеразливочний scoop were chosen followings: a diameter is 0,24 ?, a height is 0,40 ?. Foreseen thus, that the chosen capacity would provide the design of processes of interfusion for the scoops of different construction (above all things, attitudes of height of pouring of metal toward the diameter of scoop). Thus as a designing liquid used water for the temperature of 18-25оС. Choice at water as a designing liquid is explained by a circumstance that the values of viscidity of water and steel in area of temperatures of внепечной treatment are near enough to each other. Interfusions of liquid carried out the compressed air. For the imitation of slag, located on the surface of metal, utillized butter of silicon, which, as is generally known, has high values of surface-tension, and viscidity can be varied in wide enough scopes depending on his temperature. The closeness of the chosen butter of silicon made 965 ??/?3. The geometrical scale of physical models was determined taking into account the criteria of similarity of Fruda and гомохроности and 1:8 made and 1:12 in relation to the chosen designed object is setting scoop-stove by the capacity of 60т and 110т accordingly. For the visual supervision of газожидкостных streams of wall of models executed from transparent glass, and water was tinted the special indicator for a colour difference from butter of silicon. The looked after pictures of interfusion were fixed by a digital video camera. Experimental options allowed to regulate a gas expense and change position of продувных devices in relation to the vertical ax of vessel. In the process of research about 250 pictures were taken off of process of interfusion for the different values of charges and speeds of the blown gas, which change in an interval 0,1-0,8 m/ss.
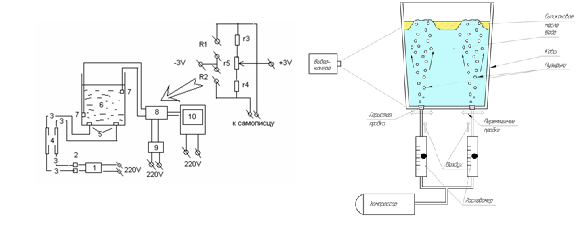
???.1 are Charts of physical models for the study of process of interfusion: and - for visualization of processes of interfusion; - for the estimation of intensity of interfusion during blowing out: 1 is a compressor, 2 is a knot of adjusting of serve of air, 3 is a pipeline, 4 - a block of measuring of parameters of the blown air (expense, pressure) of,5 is knots, 6 is a model of scoop, 7 are sensors of measuring of conductivity of water, 8 is a bridge chart, 9 - power module.
Thus, on the basis of the executed supervisions of character of motion of streams in overhead part of scoop basic hydrodynamic streams can be de bene esse classified on 5 integrated with identical terms (direction of vectors of speeds, size of speed, intensity of turbulence) area of ascending stream, penetrable through butters (to the slag); area of output of the blown gas in an atmosphere, including splashing of slag and metal (that area of spot of gas make on the surface of scoop); area of descending streams of metal, which slide along layer of slag from top to bottom; area of horizontal streams of metal (with the several of gas blisters), which move along the surface of slag to direction from an ascending stream to periphery of scoop; area of forming of mixture of metal, slag and blisters of the blown gas, which is formed under a slag layer in the area of motion of ascending streams. Development and sizes selected it is depended that of or other on the row of factors, main from which is an expense of the blown gas, amount of knots and their location, and also viscidity of
|
|
 Home
Home  Biography
Biography Українська
Українська Русский
Русский English
English